Overlapping Subfields. Miss the previous excerpt on Data Structure? Read it here: Part I.
The locations of subfields within a data structure can overlap, and the same position within a data structure can fall within the location of several subfields. A data structure declaration can use two keywords, Pos (Position) and Overlay, for these purposes.
To illustrate the concept of overlapping, or defining subfields within subfields, the following example assumes your program contains variables Firstname (15 bytes) and Phone (10 digits). The program needs to work with just the initial of the first name and with the area code, exchange, and local portions of the phone number as separate data items. Data structures let you easily access the data that way.
The Overlay keyword indicates that Initial is to be a part of Firstname rather than a subfield adjacent to it. In the preceding code, subfield Initial contains the first letter of the value of Firstname. If you code a position with the Overlay keyword, the position signals the location in the subfield where the overlay should begin. Phone is divided into three pieces accessible through subfields Areacode, Exchange, and Localnbr. Because Areacode, Exchange, and Localnbr share common space with Phone in the unnamed data structure, if your program alters the value of any one subfield, the overlapping subfields reflect that change. You can also use the Pos keyword to indicate the starting position of each subfield relative to the data structure itself:
The Overlay keyword also supports the special value *Next. Specifying *Next instead of a position begins a subfield at the next available position of the overlaid subfield field. The following code reworks the Phone example by using *Next:
When you use the Overlay keyword, the data name within the parentheses must be a subfield already defined within the current data structure. The subfield being defined must be completely contained within the subfield.
You can use Overlay to redefine subfields in a data structure with different names or data types, or both. In the following example, subfield Basedate is a native date, but Basechar is a character subfield. Both subfields occupy the same location in the data structure. If your program changes the value of one subfield, it also changes the value of the other one.
Externally Described Data Structures
The data structures discussed up to now are program-described data structures. The entire data structure description (i.e., all the subfields) is explicitly described in the program. RPG also supports externally described data structures similar to the way it handles externally described data files. The subfields in an externally described data structure follow the layout of an existing file—the subfields in the data structure have the same names, locations, and data attributes as the record format. Externally described data structures might be useful when you want to use a data structure in several different programs, when your company’s standards dictate the use of specific data structures, or when you need a data structure to mimic the layout of an existing file’s record format.
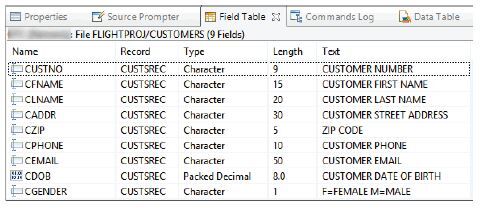
Recall from previous chapters the record layout for the example Customers file (see Figure 4.1). Here’s an example of an externally described data structure based on that file’s layout:
Often, the name of an externally described data structure is the same as the file upon which the data structure is based. The Ext (External) keyword tells the compiler that this data structure is externally described. Ext must be the first keyword following the data structure name. Because the compiler automatically acquires the subfields from the Employees file, it is not necessary to code any subfields for the data structure—all the fields in the file become subfields in the data structure. Notice that, because you need not explicitly list any subfields, the End-ds instruction can appear on the same line as the Dcl-ds instruction.
Figure 4.1: Customers file record layout
If the name of the data structure does not match the name of the file upon which it is based, the data structure definition requires the Extname (External name) keyword to explicitly name the file:
or (omitting Ext):
You can code additional program-described subfields following the data structure header, and you can use Overlay to describe subfields that overlap existing subfields in the data structure:
If you want the name of a subfield to be different from the name of the field in the external file, you can use the Extfld (External Field) keyword to associate the subfield name with the file’s field name:
To initialize an externally described data structure, use the Inz keyword. To initialize the subfields to their default values as indicated in the external file’s definition, specify Inz(*Extdft):
You can override the external default for one or more subfields by listing them with their own Inz keyword:
Qualified Data Structures
Normally, an RPG program can refer to the individual subfields in a data structure by their simple names. Those names must be unique; that is, you cannot typically have multiple data structures with identically named subfields. A qualified data structure lets you ignore that rule. When you include the Qualified keyword on a data structure header line, you create a qualified data structure.
The Qualified keyword indicates to the compiler that you will refer to the subfields in the data structure by their qualified name (i.e., the data structure name followed by a period and the subfield name). If the Qualified keyword is not used, you will refer to the subfields by their simple name, and that name must be unique. Qualified data structures can be program described or externally described, and they must be named data structures. The following examples illustrate how to define qualified data structures:
In these examples, the RPG program must refer to subfields Customer.Name or Vendor. Name to refer to the Name subfield in either the Customer data structure or the Vendor data structure. Notice that the subfields can have identical names even if they don’t have identical data attributes. In the previous examples, Customer.Id is a five-digit zoned numeric field and Vendor.Id is a seven-character field. The data structures need not have identical subfields, and the subfields need not be in the same order in each data structure. You can use qualified subfield names almost anywhere in the program that allows a variable name.
What to learn more now? Buy Programming in ILE RPG, Fifth Edition at the MC Press Bookstore today!




























 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online