It’s always best to use the right tool for the job, and for business logic, that tool is RPG.
In my last “Practical Middleware” article, I walked through a very simple program written with Node.js to read data from the IBM i. The goal was to show how easy it is to access the IBM i database. Now it’s time to continue that journey and really begin to show the power of using RPG and Node.js together.
Expanding Scope
In that previous article, I cut my full application stack down to a much simpler environment using only Node.js and SQL on the IBM i. Together those allow us to do a lot, and if you can use only a single language, then JavaScript—and more specifically, ES6 in the Node.js environment—is probably the most versatile. But if you’re reading this, you’re probably using the IBM i and almost certainly fluent in RPG. And I’m not disparaging my COBOL compatriots; everything I say here about RPG will translate to COBOL as well.
Figure 1: Taking our very simple architecture and just adding ILE RPG
Figure 1 is almost identical to Figure 1 in the previous article. The only change is that I added ILE RPG to the blue box on the left. Today we’ll see how to add RPG to the mix using functions in SQL. Why do that? Because, as I’m fond of saying, RPG is the assembly language of the relational database. That reference is getting outdated here in the new millennium, but it just means that you can do things in RPG that can’t be done cleanly in other languages. Most importantly, RPG is very good for allowing completely different paths for data access based on data conditions, something that tends to give SQL problems.
I’ve always been a fan of Java because of its strict object orientation. I always had a little trepidation when dealing with JavaScript because it is a loosely (or dynamically) typed language. These days, though, the more I work with modern JavaScript (ECMAScript 2015, more popularly known as ES6), the more I appreciate its virtues as well. In fact, the object-oriented features of ES6 are so strong and so critical that I recommend you have a solid object-oriented background before starting to write complex applications using JavaScript. For a good intro, you can start here. And as an additional bit of flavor, a statically typed version of JavaScript is available called TypeScript.
Adding to the Stack
We want to add RPG business logic to our program stack. Our goal is to be able to pass complex, structured data between the layers. Traditionally, in the midrange world, we do this with a data structure, so our initial objective is to write a program that accepts a customer number and passes back a data structure and then access that program from our Node.js layer. Shortly we’re going to explore the modern alternative to data structures, JSON data, but that’s a little later.
Please note that SQL’s limited capabilities with numeric data can be a problem when interacting directly with RPG. RPG defaults numeric data to packed decimal, which corresponds to SQL’s NUMERIC data type. Zoned decimal, on the other hand, has no direct analog in SQL and instead presents as character data. It’s even trickier because RPG will automatically recast zoned data to packed unless you tell it not to, so you have to be mindful of your data types.
Back to our project. We can now write a simple program. This program will have two parameters: an input parameter for the customer number and an output parameter for the data. As noted above, the output data is a data structure. I’ve hardcoded its length because I know the lengths of the fields, but that means I have to be careful to keep track of the fields included. That’s a maintenance burden long term, but there are ways to get around it. We’ll see more of that in upcoming articles.
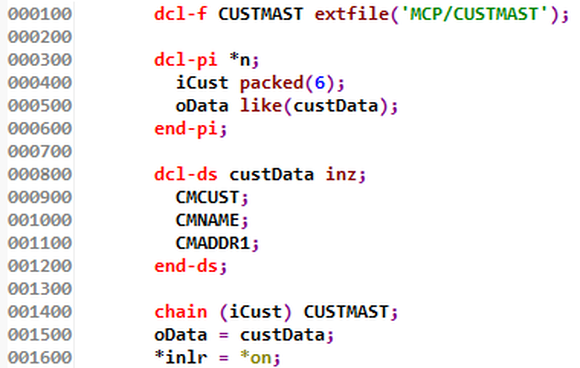
Figure 2: RPG program GETCUST, which returns data from the customer master file
The program truly is simple. It chains to the CUSTMAST file using the customer number passed in and returns some of the data. You may notice a couple of things. First, I hardcoded the library name for the file using the extfile keyword. While that avoids the complexities of library lists in our ODBC connection, it obviously has scalability and testing issues. But it’s fine for our proof-of-concept programming. Second, I take advantage of RPG conventions to get the data into the data structure. But be aware that the customer number is defined as zoned in the file, which allows it to appear in the data structure as if it’s character data. That’s definitely a cheat, but we’re going to be using that cheat only for a short period.
One thing to note is that there is very little error handling. As we progress in our design, I’ll spend a lot more time on how to handle errors in a consistent fashion, but for now what’s going to happen is that because I’ve initialized the custData data structure with the inz keyword in line 800, if the CHAIN fails the program will return zero in the CMCUST element of the data.
Wrapping It Up
No, not the article! The program! I’m going to wrap the RPG program in a function so that it’s easily accessible from SQL. Remember that the concept behind any object-oriented function is that it can accept zero or more parameters, but it returns only a single value, thus the need for a data structure to return all the data requested.
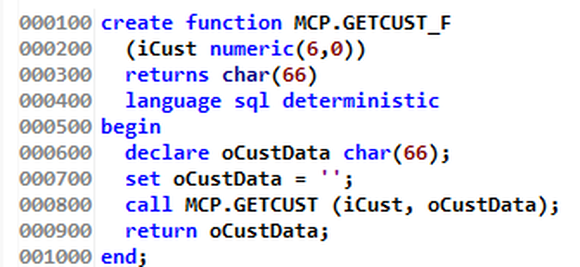
Figure 3: SQL function GETCUST_F, which calls program GETCUST
The function wrapper is very simple, and we can use this template for any call. Identify all the input parameters and create a dummy variable for the return data. Specifically in this case, line 300 identifies that the function is returning 66 characters of data, line 600 creates a temporary variable to pass to GETCUST (so it can get loaded), and line 900 returns the data we got from the RPG program. So line 1500 in Figure 2 loads the data that is returned in line 900 of Figure 3. Easy!
Modify the JavaScript
The last step for today is to modify the JavaScript code in our Node.js program to use the new function. The changes are actually quite minimal.
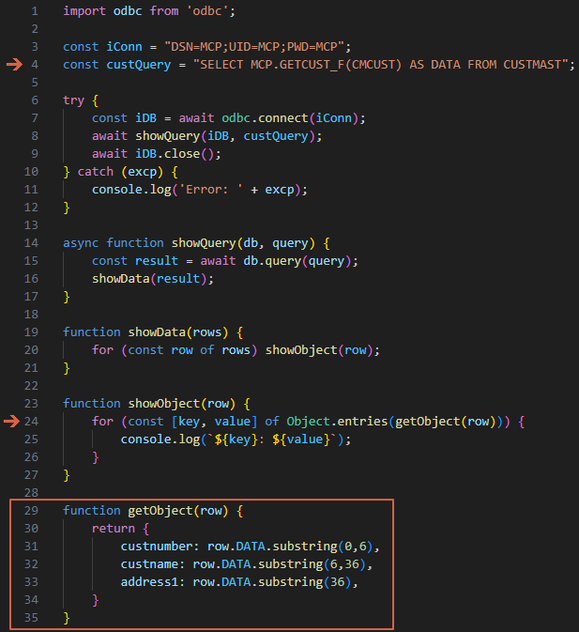
Figure 4: The modified program that uses our new RPG function
Please refer back to the original article to get an in-depth explanation of the first 27 lines, but the CliffsNotes version is that we connect to a data source we’ve configured for our IBM i, run an SQL statement, and then dump the records returned from the query to the console. And now, even though we’ve completely changed the underlying architecture, only two lines of the original code (the indicated lines 4 and 24) have changed. The only additional logic is the new getObject function, which converts the data structure received from the RPG program to an object that can be dumped by showObject. Let’s review what happens there.
In the original code, the showQuery function returns the results of the function db.query. This is an array of objects, each one representing a row from the query. Each of these objects contains an element from the query, which in the case of the original code were the fields CMCUST, CMNAME, and CMADDR1. The way the odbc package works, the element names match the field names in the SELECT statement, and that’s what we saw in the output:
Figure 5: The output of the previous program using the column names as the element names
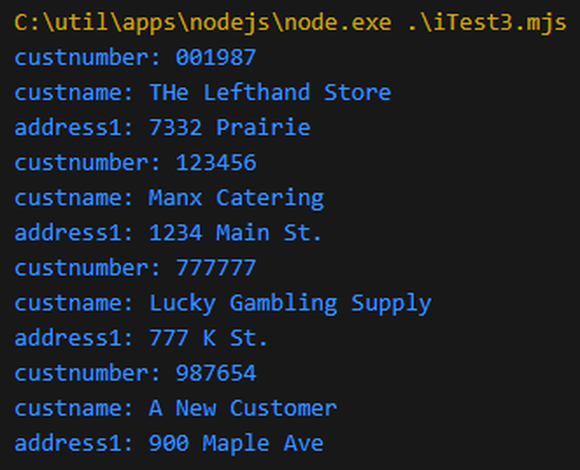
The fundamental change in this version is that each row passed to showObject actually has only one element, named DATA, which needs to be parsed into the individual fields. In this version, the DATA value returned from the function is the data structure from the program GETCUST, which has data in fixed positions. The new getObject function parses that data into a new object with elements whose names are defined in the getObject function, but the results are quite similar:
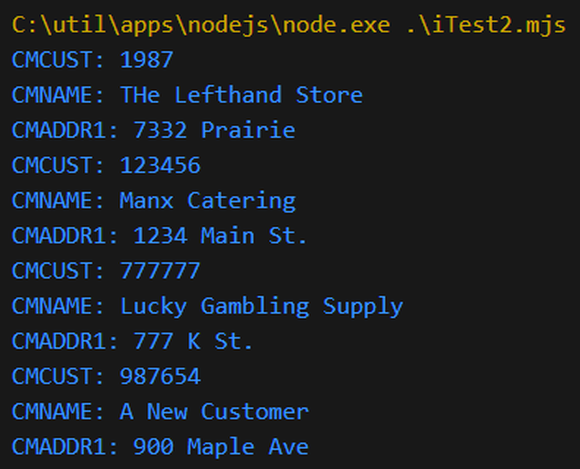
Figure 6: The output of the new programs
And there you go! Now, you may be asking yourself why we went to all this trouble just to basically get the same result. And while it’s true that the data is fundamentally the same, there is a distinct difference. Since the data was built by an RPG program, that program could have done anything, from calling another RPG program to reaching out to another server, to populate any of the data points. We are no longer constrained by just what is in the database and what can be done using SQL syntax. We’ve unleashed all the power of RPG for building business logic and can now do anything we need to do to get data for our users.
One other small detail you may have noticed is that the element names were different: custnumber instead of CMCUST, and so on. If you look closely at the code, you’ll see that those element names are hardcoded in lines 31-33 of Figure 4. Don’t worry too much about it because we’ll be revisiting that whole concept in the next installment, but I wanted you to be aware of that difference.


















 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online