Learn a creative technique that Gene Gaunt invented to retrieve all system built-ins supported by your IBM i.
Since System/38, as a high-level machine interface, the Original Machine Interface (OMI) instruction set described a complete, elegant object-based architecture of the system. The OMI instruction stream, along with other components (e.g., the object definition table (ODT)) stored in the program template of an MI program object, allows the MI program to be translated for future hardware platforms with no need of re-compilation.
In V2R3, a new machine instruction set, the New MI (NMI) was introduced to AS/400 along with the Integrated Language Environment (ILE), which leads to a new (ILE) program model, a new (ILE) process model, and a series of new (ILE) compilers. Just like the OMI program template stored in an OMI program object, an NMI program template can be stored in an ILE program object, which allows the ILE program to be translated for future hardware platforms. An NMI program template is composed of components such as the Module Dictionary Component and the Module Instruction Component, which contains the NMI instruction stream.
If you scrutinize the NMI instruction stream in the System Service Tools (SST) dump of an ILE program object or module object, you will find that it is hard to find NMI instructions directly related with the object-based architecture of IBM i except the Call Program (CALLPGM) NMI instruction. It seems that almost all of the NMI instructions are platform-neutral. So where did the IBM i-specific instructions go? The answer is the CALLBI (Call Built-in Function) NMI instructions in the NMI instruction stream generated for an ILE program or module object. The CALLBI NMI instruction calls are what IBM documentation refers to as "MI instructions that are supported in Bound Programs"—in other words, the system built-ins. The CALLBI NMI instruction takes four operands, the third of which is referred to as the "built-in number" in IBM-provided MI documentation. For example, the NMI instruction equivalent to an OMI instruction GENUUID uuid-return-template; might look like the following (the value of operand-3 461 is the system built-in number of the GENUUID instruction):
|
OFFSET 00000A40 OPCODE CALLBI OPERAND 1 88 OPERAND 2 1 OPERAND 3 461 OPERAND 4 0 |
In NMI, the majority of the complex MI instructions become invocations to system built-ins via the CALLBI NMI instruction.
Although it's hard to find public documentation about how programs written in ILE high-level languages (HLLs) are compiled into NMI program templates and finally translated into PowerPC machine code, you can discover the following facts through the discussion threads in the MI400 mailing list (for example, by searching for the "optimizing translator" and "MI transformer" keywords):
- Today, there is only one MI translator. The NMI translator (aka the Optimizing Translator) accepts the NMI program template and translates it into the final PowerPC machine code.
- OMI program templates are converted into NMI program templates by the MI transformer and then passed to the NMI translator. Note that the program template stored in an OMI program compiled by an OPM HLL compiler is an OMI program template, which reserves the possibility for the OMI program to be re-translated and run on an earlier AS/400 VRM (or even the System/38) that doesn't know NMI. Nowadays, newly added MI instructions are only available as system built-ins. It seems that the MI transformer has not been maintained for newly added MI instructions. Please refer to the "What's new" section in the MI documentation for different VRMs. For example, What's new for IBM i 7.1.
- From a post in the MI400 mailing list (back in 1999)by MI guru David McKenzie , we know that the QSYS/QWXCRTMD program accepts W-code generated by ILE HLL compilers for a module object, yields the NMI program template, invokes the NMI translator to translate the NMI program template into PowerPC machine code, and finally encapsulates the NMI program template and the PowerPC machine code into the resulting module object.
As far as I can tell, what happens when you compile a module is
that the compilers generate _object_ W-code (in binary form, as
opposed to human-readable source), which they pass to a pgm called
QWXCRTMD, which translates to object NMI and calls the translator
(which is in SLIC) to create the PowerPC machine code. This is in
contrast to the OPM compilers. They generated _source_ MI and
passed it to the MI "assembler", QPRROOTP. That's why we can have
the QPRCRTPG API--it's just a front-end to the same sourcecode
"assembler" that the compilers use. However, it appears that a
sourcecode assembler for NMI doesn't exist on the system. To have
one, we'd have to pay IBM the $1M or write it ourselves. Anyone
want to dust off YACC or Bison?
Obviously, the QWXCRTMD program knows all the system built-ins, since it is responsible for generating calls to system built-ins in the form of the CALLBI NMI instructions with the corresponding system built-in number.
Also a sad fact is that the current publically documented MI instructions are only a small part of the entire MI. Simon Coulter said in a post in the MIDRANGE-L mailing list:
> Lets say you wanted to write your own operating system to
> replace OS/400. What kind of hoops would you have to jump
> through to get THAT kind of info from IBM? Or couldn't get get
> them at all?
This was certainly possible on the S/38 where documentation in the
form of the S/38 Functional Concepts manual, S/38 Functional
Reference Vol 1, and S/38 Functional Reference Vol 2 would have
provided most, if not all, you need to know about the MI level.
The proviso is that you would build your OS on top of the LIC.
It is harder on the AS/400 because Rochester have blocked the MI
instructions they feel we don't need to know about (e.g.,
source/sink instructions so that pretty much buggers up any I/O
routines) and provide only an expurgated version of the MI
reference.
Nevertheless, there is still one possible way to see a more complete set of IBM-supported MI instructions (system built-ins) via a technique invented by Gene Gaunt. This technique retrieves the system built-in information stored in the QWXCRTMD program. The following is Gene's post from 2005 that describes this technique via a Rexx program that prints information, such as system built-in name and system built-in number, about all the system built-ins in VRM530.
print ILE built-in functions, V5R3-specific
* Subject: print ILE built-in functions, V5R3-specific
* From: gene_gaunt@xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx>
* Date: Tue, 14 Jun 2005 12:20:13 -0400
* List-archive: <http://archive.midrange.com/mi400>;
* List-help: <mailto:
* List-id: MI Programming on the AS400 / iSeries <mi400.midrange.com>
* List-post: <mailto:
* List-subscribe: <http://lists.midrange.com/mailman/listinfo/mi400>;, <mailto:
* List-unsubscribe: <http://lists.midrange.com/mailman/listinfo/mi400>;, <mailto:
As you know, my old print program for MI built-in functions no longer
works, since IBM removed the user space that contained the function names.
But, for V5R3 at least, here is my rewrite that *will* work. Note that
beyond V5R3, the three specific values below (665, 22A0, and 3980) will
probably need changing.
/********************************************************************/
/* PROGRAM - PRTBUILTIN */
/* FUNCTION - print the ILE built-in functions, V5R3-specific */
/* LANGUAGE - REXX */
/* AUTHOR - Gene Gaunt */
/********************************************************************/
"crtsavf file(qtemp/stdin)"
"savobj obj(qwxcrtmd) ",
"lib(qsys) ",
"objtype(*pgm) ",
"dev(*savf) ",
"savf(qtemp/stdin) ",
"updhst(*no) ",
"dtacpr(*no)"
"ovrdbf file(stdin) ",
"tofile(qtemp/stdin)"
"ovrprtf file(stdout) ",
"tofile(qsysprt) ",
"splfname(prtbuiltin)"
data = ''
do forever
parse linein record
if record == '' then leave
data = data || left( record, 512 )
end
walk = c2d( substr( data, X( 75 ), 3 ))
walk = c2d( substr( data, X( 1D ) + walk, 3 ))
walk = c2d( substr( data, X( 75 ) + walk, 3 ))
walk = c2d( substr( data, X( 45 ) + walk, 3 ))
walk = c2d( substr( data, X( 665 ) + walk, 3 )) + X( 0 )
name = walk + x2d( 22A0 )
code = walk + x2d( 3980 )
do while walk < name
AA = c2d( substr( data, walk, 4 ))
BB = c2d( substr( data, walk + 4, 2 ))
CC = c2d( substr( data, walk + 6, 2 ))
DD = c2d( substr( data, walk + 8, 2 ))
EE = c2d( substr( data, walk + 10, 2 ))
if BB == 0 then leave
show = left( substr( data, name + AA, BB ), 20 )
do DD while EE == 0
show = show ||,
right( c2d( substr( data, code + CC * 4, 4 )), 6 )
CC = CC + 1
end
say show
walk = walk + 12
end
return
X: return x2d( 5001 ) + x2d( arg( 1 ))
The source of the Rexx program for VRM530, prtbuiltin.rexx, is available here. The VRM540 version of this program, prtbltin54.rexx, is available here. The output of prtbltin54.rexx is available in Appendix A, System Built-ins at VRM540, which you can download here.
The steps of Gene's solution are the following:
- Save the QWXCRTMD program into save file QTEMP/STDIN.
- Override the input file of the Rexx program (STDIN) to save file QTEMP/STDIN so that the Rexx program can read the content of the save file.
- Locate and parse the system built-in information in QWXCRTMD.
Now let's go through the steps of Gene's solution one by one and implement these steps in CL and RPG. As mentioned in Gene's post, some of the "specific values" probably changed from release to release due to the changes to the number of system built-ins or even the changes to the format of program objects. And the "specific values" used in this article are specific to VRM540 of IBM i.
Save the QWXCRTMD Program into a Save File
The first step is to save the QWXCRTMD program into a save file. Consider using the DTACPR(*NO) parameter when issuing the SAVOBJ command to ensure that the content of the QWXCRTMD program in the resulting save file remains unchanged. Save files allow a user to break the limitation brought by the object-based architecture of IBM i for object integrity. As an object-based system, in IBM i a user is not allowed to access the encapsulated part of an MI object except through proper MI instructions defined for that kind of MI object. However, when an MI object is saved in a save file, a user can read the content (either the encapsulated part or the possible associated spaces of it) in the manner of reading a file object. For a similar reason, save files can bring other risks. For example, MI objects saved in a save file can be read by a user who is unauthorized to the saved MI objects (providing that the user is authorized to the save file itself). However, as an offline-storage mechanism designed for backup and object replication, save files should not be blamed. What is important here is that save files can help us to "look into" the encapsulated part of the QWXCRTMD program.
The following couple of CL commands create a save file named CRTMD in the QTEMP library and then save the QWXCRTMD program into it. Run these commands directly or compile them into a CL program and then run the CL program.
|
CRTSAVF FILE(QTEMP/CRTMD) SAVOBJ OBJ(QWXCRTMD) LIB(QSYS) DEV(*SAVF) OBJTYPE(*PGM) SAVF(QTEMP/CRTMD) DTACPR(*NO) |
Read the Content of the QWXCRTMD Program from Save File QTEMP/CRTMD
In prtbuiltin.rexx, Gene overrides the input file of the Rexx program (STDIN) to the save file containing the QWXCRTMD program. We can write a simple RPG program to read the save file and write the content of the QWXCRTMD program into the User Space (*USRPSC) object QTEMP/CRTMD so that we can check the content of QWXCRTMD by dumping the CRTMD user space to a spooled file (e.g., via a DMPOBJ QTEMP/CRTMD *USRSPC command). The content of the only MI object saved in save file CRTMD is started from offset hex 5000 in the data that can be read from save file CRTMD. So we should skip the first hex 5000 bytes of data when reading save file CRTMD. Also note that only the first 512 bytes of a 528-byte save file record are valid save file data.
The following is the source of CRTMDR01, crtmdr01.rpgle.
|
h dftactgrp(*no)
fCRTMD if f 528 disk /copy mih-ptr d rec ds d rcd 512a d 16a d ds d oddptr * procptr d spc16 * overlay(oddptr) d spp s * d ch512 s 512a based(spp) d off s 10u 0 inz(0)
/free rslvsp_tmpl.obj_type = x'1934'; rslvsp_tmpl.obj_name = 'CRTMD'; rslvsp2(spc16 : rslvsp_tmpl); spp = setsppfp(oddptr);
read CRTMD rec; dow not %eof(CRTMD); off += x'0200';
if off > x'5000'; // Content of QWXCRTMD ch512 = rcd; spp += 512; endif;
read CRTMD rec; enddo; *inlr = *on; /end-free |
Call the Create User Space (QUSCRTUS) API to create the CRTMD *USRSPC in library QTEMP.
|
CALL PGM(QUSCRTUS) PARM('CRTMD QTEMP' 'CRTMD' X'00200000' /* Size of space */ X'00' '*ALL' 'Content of *PGM QWXCRTMD') |
Then call CRTMDR01 to read the content of the QWXCRTMD program from the save file and write it into the CRTMD space. Now, with the help of the save file trick, we've copied the content of the QWXCRTMD program (including its encapsulated part, which is usually not accessible by a user or program) to a user space object.
Locate and Parse the System Built-in Information in QWXCRTMD
The system built-in information is stored in one of the prototype strings (with index number 69) in the NMI program template of QWXCRTMD. For simplicity, we will refer to the prototype string that contains the system built-in information as PSTR-69.
The following table describes the steps by which the Prototype String Desc Sublist component can be located within the encapsulated part of an ILE program. The contents shown below are extracted from the SST dump of the QWXCRTMD program at VRM540.
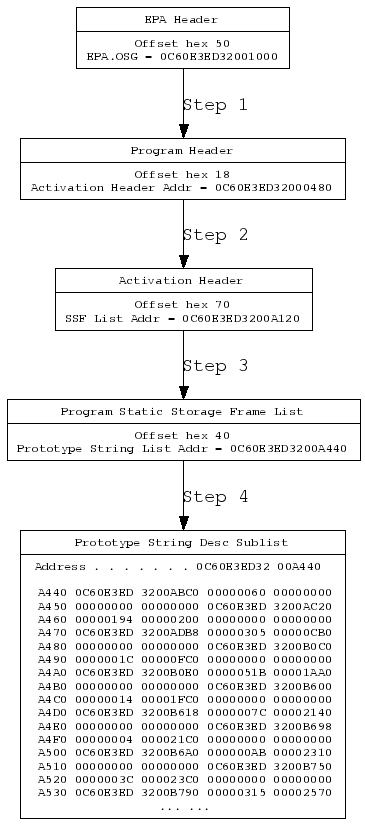
Figure 1: Locate the prototype string Desc Sublist Component in the encapsulate part of QWXCRTMD. (Find more code here.)
The Steps
- Locate the 8-byte Single-Level Store (SLS) address of the Program Header via the OSG field in the EPA header. The EPA.OSG field is at offset hex 50 from the beginning of the EPA header.
- Locate the 8-byte SLS address of the Activation Header via the ACT HDR PTR field (address of the Activation Header) in the Program Header (at offset hex 18).
- Locate the address of the Program Static Storage Frame List via the FRAME LIST PTR field (at offset hex 70) in the Activation Header.
- Locate the address of the Prototype String Desc Sublist via the PROTO STR PTR field (at offset hex 40) in the Program Static Storage Frame List.
Following these steps, we can finally locate the Prototype String Desc Sublist of the QWXCRTMD program.
Note that the OSG field in the EPA header for most types of MI objects is the object address (aka the address of the base segment of the MI object); however, the EPA.OSG field for an MI program object (a hex 0201 program, a hex 0202 SQL package, a hex 0203 service program, or a hex 0250 Java program) is the address of the program header of the program object.
The Prototype String Desc Sublist is filled with 24-byte entries that describe each prototype string in the following format:
- 8-byte address of the prototype string
- BIN(4) length of the prototype string
- BIN(4) MSSF OFFSET
- CHAR(8) Reserved (hex 00)
So the offset of PSTR-69 from the beginning of the Prototype String Desc Sublist of the QWXCRTMD program can be calculated via the following formula:
|
Offset-PSTR-69 = 24 * (69 - 1) = 1632 = hex 660 |
Now we have enough information to locate PSTR-69 in the encapsulated part of QWXCRTMD. Procedure locate_pstr69 in the example RPG program crtmdr02.rpgle (shown below) implements the above-shown steps.
After locating PSTR-69, let's investigate the system built-in information stored in it. PSTR-69 consists of three sections: offset/length, name (containing the system built-in names), and code (composed of 4-byte code values, up to 5 code values for an individual system built-in). At VRM540, the lengths of these sections are hex 22B0 bytes, hex 16F0 bytes, and hex 3504 bytes, respectively. I don't know how to determine the length values of these sections programmatically. I obtain these length values at VRM540 by checking the content of PSTR-69 in the SST dump of the QWXCRTMD program.
The format of each 12-byte entry in the offset/length section is the following:
- BIN(4)—Offset of the system built-in name in the name section
- BIN(2) —Length of the system built-in name
- BIN(2) —Offset (in 4-byte units) of the code values of the system built-in in the code section. There can be up to 5 code values of a single system built-in.
- BIN(2) —Number of code values for the system built-in
- BIN(2) —Gene named this field EE in his original Rexx program
An example RPG program, crtmdr02.rpgle, locates PSTR-69 in the content of the QWXCRTMD program stored in user space QTEMP/CRTMD, parses the system built-in information in PSTR-69 following the above-described format of PSTR-69, and finally writes the parsed system built-in information to a spooled file.
Call CRTMDR02, and the output is shown as in Appendix B, System Built-ins at VRM540, which you can download here (retrieved via CRTMDR02). As an example, I extracted the Resolve Data Pointer instructions and the Resolve System Pointer instructions from the output of CRTMDR02 as the following:
|
Built-in Name Code-1 Code-2 Code-3 Code-4 Code-5 CC EE(Hex) _RSLVDP1 00097 00000 00000 00385 00006 _RSLVDP2 00097 00000 00000 00385 00004 _RSLVDP3 00097 00000 00000 00385 00000 _RSLVSP1 00097 00000 00000 00030 00014 _RSLVSP2 00097 00000 00000 00030 00012 _RSLVSP3 00097 00000 00000 00030 00010 _RSLVSP4 00097 00000 00000 00030 00008 _RSLVSP5 00097 00000 00000 00030 00006 _RSLVSP6 00097 00000 00000 00030 00004 _RSLVSP7 00097 00000 00000 00030 00002 _RSLVSP8 00097 00000 00000 00030 00000 |
Note that the Code-4 code value of a system built-in is the system built-in number. The built-in number is available in the "Bound program access" box in IBM's MI documentation. Code-4 is also useful for telling which actual MI instruction (system built-in) is invoked by a CALLBI NMI instruction. As mentioned, The CALLBI NMI instruction takes four operands, the third of which is the system built-in number of the system built-in to invoke. The Code-5 code value is also related with the CALLBI NMI instruction. It is specified as the fourth operand (operand 4) of a CALLBI NMI instruction to uniquely determine which system built-in to invoke in combination with the system built-in number (operand 3 of CALLBI). For example, the built-in numbers of all the Resolve System Pointer system built-ins (_RSLVSP1 to _RSLVSP8) are 30; however, their Code-5 values (specified as operand 4 in the generated NMI CALLBI instructions) are different. The following is a simple ILE C procedure that invokes _RSLVSP1 and _RSLVSP4:
|
# pragma linkage(_RSLVSP1, builtin) void _RSLVSP1(void**); # pragma linkage(_RSLVSP4, builtin) void _RSLVSP4(void**, void*, void**);
void *p = NULL; void *q = NULL; void *c = NULL;
void f() { _RSLVSP1(&p); _RSLVSP4(&p, q, &c); } |
The NMI CALLBI instructions generated for invocation to _RSLVSP1 and _RSLVSP4 are the following (note operand 3 and operand 4 of the CALLBI instructions):
|
# CALLBI instruction generated for _RSLVSP1 OFFSET 000000CC OPCODE CALLBI OPERAND 1 5 OPERAND 2 1 OPERAND 3 30 OPERAND 4 14 # CALLBI instruction generated for _RSLVSP4 OFFSET 0000013C OPCODE CALLBI OPERAND 1 8 OPERAND 2 3 OPERAND 3 30 OPERAND 4 8 |
Gene's prtbuiltin.rexx program does not process the system built-ins whose EE field is hex 0000. From the output of crtmdr02.rpgle (Appendix B below, System Built-ins at VRM540 (retrieved via CRTMDR02)), you can find out that there are 55 of this kind of system built-ins. The common features of the offset/length fields of these system built-ins are:
- The num_codes (number of code values) field is zero.
- The code_offset field is used to record an index value for all system built-ins whose EE field is not hex 0000.
In Appendix B, the index value and the value of the EE field of these system built-ins are listed in column CC and EE(Hex).
Additional investigation seems to indicate another feature of this kind of system built-ins: Unlike common system built-ins that are translated into NMI CALLBI instructions, these system built-ins are inlined in the result NMI instruction stream. (I didn't test all of those 55 system built-ins.) For example, compile the following ILE C procedure and check the NMI instruction stream in the SST dump of the resulting module object or program object:
|
# pragma linkage(_min4, builtin) int _min4(int, int);
static int a = 1, b = 2, c = 0; void f() { c = _min4(a, b); } |
You'll find that the NMI instructions generated for the C statement c = _min4(a, b); might look like the following:
|
OFFSET 000000AC OPCODE LOD1 OPERAND 1 1 OFFSET 000000B4 OPCODE LOD1 OPERAND 1 2 OFFSET 000000BC OPCODE MIN OFFSET 000000C0 OPCODE STR1 OPERAND 1 3 |
Change the Program Logic by Modifying the NMI Instruction Stream
I greatly appreciate Gene's creative technique that allows me to see a more complete machine interface of the IBM i. The output of the technique will definitely help the developers who love this platform and are eager to understand this platform . At the end of this article, I will demonstrate a tiny experiment that is dependent on the system built-in numbers retrieved by Gene's technique—changing the invocation of system built-in _XORSTR to system built-in _ANDSTR in a program by modifying the NMI instruction stream.
Look at the following ILE C program, ii403.c, that XORs (exclusive or) two EBCDIC character strings and prints the resulting string in hexadecimal form.
|
# include <stdlib.h> # include <stdio.h>
# pragma linkage(_XORSTR, builtin) void _XORSTR(void*, void*, void*, unsigned);
static char *_a = "ABCD"; /* hex C1C2C3C4 */ static char *_b = "abCd"; /* hex 8182C384 */ static char *_c = " ";
void i_proc() { _XORSTR(_c, _a, _b, 4); }
int main() { i_proc(); printf("Result string (hex): %08X\x25", *(int*)_c); return 0; } |
The output of II403 is as we expected (XOR hex C1C2C3C4, hex 8182C384 = hex 40400040):
|
Result string (hex): 40400040 |
In the SST dump of program object II403, locate the CALLBI NMI instruction generated for the system built-in _XORSTR in the Module Instruction Component. (The operand 3 of the CALLBI NMI instruction (built-in number) is 453.)
|
OFFSET 000000F8 OPCODE CALLBI OPERAND 1 6 OPERAND 2 4 OPERAND 3 453 OPERAND 4 0 |
Follow the offset value hex 000000F8 into the NMI instruction stream. You find out that the address of operand 3 of the CALLBI instruction is 15FC166401 001894.
|
15FC166401 001860 +00E0 000000020000001B 0000000300000071 0000000500000002 0000001B00000046 15FC166401 001880 +0100 0000004D00000004 0000006100000006 00000004000001C5 0000000000000012 |
Change the 4-byte built-in number from hex 0000001C5 (453) to the system built-in number of _ANDSTR, hex 000001C2 (450). Start the SST session and select the following menu items one by one:
|
1. Start a service tool 4. Display/Alter/Dump 1. Display/Alter storage 5. Starting address |
In the Specify Address display, enter 15FC166401 001894 and press Enter. In the Display Storage display, change the 4-byte value at address 15FC166401 001894 from hex 0000001C5 to hex 000001C2 and press function key F11 twice.
After changing the NMI instruction stream of program II403, the last step is to let the program object be translated again according to the newly changed NMI program template. To achieve that, simply issue a Change Program (CHGPGM) command with the USRPRF parameter set to a value different from the value specified when the II403 program was created in order to let the system translate the NMI program template stored in II403 into machine code and re-create the program object. Assume that II403 was created with a CRTBNDC ... USRPRF(*USER) command. You can now issue a CHGPGM II403 USRPRF(*OWNER) command.
Now call II403 to check the result of our tiny experiment. The output of the changed II403 would look like the following:
|
Result string (hex): 8182C384 |
That's the expected result of our experiment: AND hex C1C2C3C4, hex 8182C384 = hex 8182C384.












 IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn: Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online