At the most basic level, an application is a computer program that has been designed to perform a group of coordinated operations to solve a particular problem. Consequently, all applications are constructed around five basic elements.
Editor's Note: This article is excerpted from chapter 6 of QuickStart Guide to Db2 Development with Python, by Roger Sanders.
Those elements are:
- Input
- Logic (decision control)
- Memory (data storage and retrieval)
- Arithmetic operations (calculations or processing)
- Output
Input is defined as the way an application receives the information it needs to produce solutions for the problems it has been designed to solve. Once the appropriate input is received, logic takes over and controls what information (data) should be placed in or taken out of memory and what arithmetic operations should be performed on that information. (Because data placed into or taken out of memory is not persistent and can be lost if not physically stored somewhere else, applications often interact with the operating system to move data to and from simple character or byte-oriented files.) Finally, when the application has generated a solution to the problem it was designed to solve, it provides output in the form of an answer or specific action.
Applications that work with Db2 still contain these basic elements; the only real difference is the way in which persistent data is stored and retrieved, and in some cases, the way logic is exercised. File input/output (I/O) operations are replaced with SQL operations, and in some cases, decision control can be built directly into a Db2 database in the form of a trigger, stored procedure, or constraint. But, because of this difference, Python applications that use a Db2 database for persistent storage must perform three distinct tasks that are not required by more traditional applications:
- Establish a connection to a Db2 server or database
- Perform any transaction processing required (using SQL)
- Terminate the connection when it is no longer needed
Additionally, Python applications that work with Db2 often perform other tasks like obtaining information about a specific database or retrieving Db2-specific error messages when a desired Db2 server or database operation fails.
Functionality Provided by the ibm_db and ibm_db_dbi Python Libraries
In Chapter 4, “Python and Db2,” we saw that there are two Python libraries that are used primarily to build Python applications that interact with Db2 servers and databases: the ibm_db library and the ibm_db_dbi library.
And, in Chapter 3, “The Db2 Call Level Interface,” we learned that many of the APIs found in the ibm_db library are similar to those found in the Db2 CLI driver. Table 6.1 shows the APIs available with this library, along with their purpose.
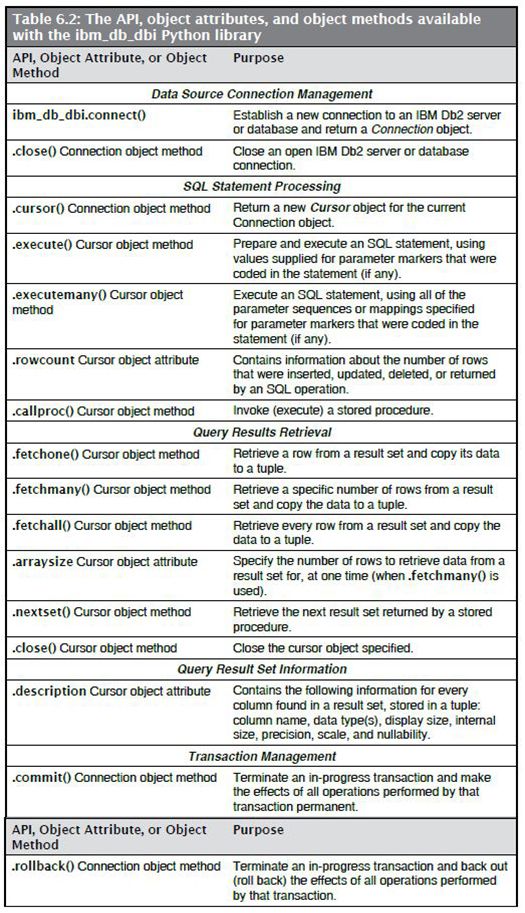
Because the ibm_db_dbi library adheres to the PEP 249 — Python Database API Specification v2.0, it contains only one API: the ibm_db_ dbi.connect() API. Once executed, attributes and methods associated with the Connection object this API returns can be used to perform basic operations against the connected Db2 server or database.
Table 6.2 provides Information about the ibm_db_dbi.connect() API, along with a list of the object attributes and methods that are available with the ibm_db_dbi library.
Special Objects Used by Db2-Python Applications
Db2 CLI/ODBC applications rely on special data storage areas to interact with Db2 servers and databases—these storage areas are identified by unique handles, which are simply pointer variables that refer to data objects controlled by Db2 CLI or the ODBC Driver Manager. Use of these storage areas frees Db2 CLI/ODBC applications from having to allocate and manage global variables and Db2-specific data structures.
Because the Db2 CLI driver serves as the foundation for the ibm_db and ibm_db_dbi Python libraries, both of these libraries rely on similar special data objects to interact with Db2 servers and databases. With the ibm_db library, IBM_DBConnection and IBM_DBStatement objects are used; with the ibm_db_dbi library, Connection and Cursor objects are used instead. As the name implies, IBM_DBConnection and Connection objects are used to store information about a Db2 server or database connection, such as:
- The current state of the connection being managed
- The current value of each connection attribute available
- Diagnostic information about the connection the object refers to
On the other hand, IBM_DBStatement and Cursor objects are used to store specific information about a single SQL statement (and its associated cursor, if any), such as:
- The current value of each SQL statement attribute available
- The addresses of application variables that have been bound to (associated with) parameter markers coded in the SQL statement the object refers to
- Diagnostic information about the SQL statement the object refers to
Stay tuned for Part 2, coming soon in an upcoming issue of MC TNT. Can't wait? You can pick up Roger Sander's book, QuickStart Guide to Db2 Development with Python, at the MC Press Bookstore Today!



























 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online