Menu documentation doesn't have to be boring anymore.
If you use User Interface Manager (UIM) menus to create your System i menus, you're probably already aware of the ability to use help panels to define your menu help. What you may not be aware of is that you can actually create much more dynamic menu documentation. In this tip, we'll explore how you can display an HTML document or PDF file instead of the old "green-screen" help text when your users press the Help key.
UIM Menus
If you create your menus through the screen design aid (SDA) menu creation utility, you probably aren't aware of what UIM menus are and what they can offer to you. UIM allows you to create menus that replicate standard IBM menus. Unlike SDA menus, UIM supports multi-page menus. When creating menus using UIM, you can also create menus with user-defined command keys. This powerful feature allows us to launch custom help from a System i menu. While an SDA menu is made up of two source members—the MNUDDS, which contains the screen display information, and the MNUCMD, which contains the commands executed by each command—all of the information required to generate a UIM menu is contained in a single MENU source file. When creating a menu using UIM, the following objects are created:
- Panel group objects
- Menu objects
- Search index objects
The panel group and menu objects contain panel definitions and online help information. A menu object (*MENU), which contains a panel group definition, is created using the TYPE(*UIM) parameter on the Create Menu (CRTMNU) command. The panel group and menu objects are created using a tag-based language that specifies definitions for UIM elements. The UIM creates search index objects that contain search terms extracted from online help information. A search index object makes it more efficient for a user to locate specific online information using the index search function.
Elements Within a Panel Group
The tag-based language used to define the panels, menus, and online help also supports definitions of symbolic elements that include the following:
- Variable classes
- Data elements that can be accessed through the UIM application programming interface (API), such as dialog variables and lists
- Variable records that define buffers passed by application programs
- Conditional expressions that must be true if certain processing is to take place
- Key lists containing the definition of function keys
- Menu bars containing the definition of one or more pull-down menus
- Panel definitions containing one or more areas to present data, information, lists, and menus
- Online help text modules
Menu Panel Source Definition
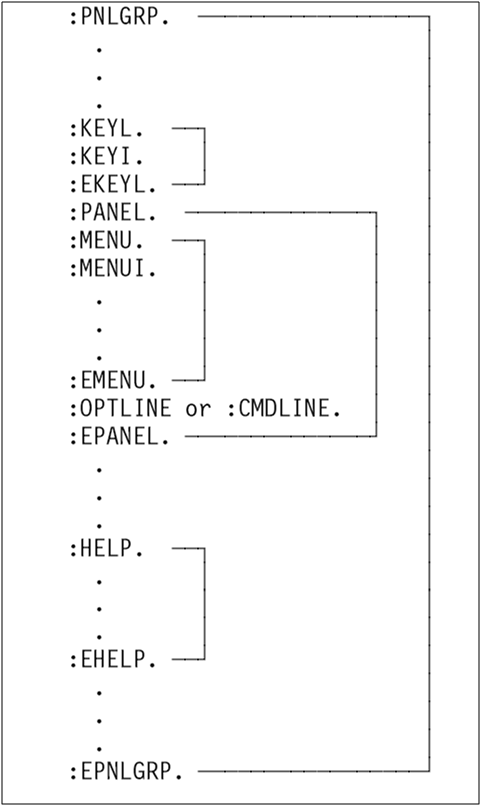
To define UIM menus, we use a nested tag system. The figure below shows the tags required to create a UIM menu and its nesting levels.
Figure 1: UIM menus use a nested tag system.
The KEYL Tag
The KEYL tag is used to define key lists, which identify the function keys available on the menu. The EKEYL tag identifies the end of the key list group. The KEYL tag has one required and one optional attribute.
Required Attribute
NAME=key-list-name. The name assigned to the key list.
Optional Attribute
HELP=help-module-name. Links to the help information associated with a given menu item. The associated help text will be defined in a panel group located elsewhere in the menu source or can be imported from another panel group.
The KEYI Tag
Individual key definitions within the key list are defined using the KEYI (key list item) tag. One or more KEYI tags may be defined within a KEYL group. The KEYI tag defines a single function key. This tag occurs between the KEYL and EKEYL tags. It defines the text to be displayed for a key and defines what to do when that key is pressed.
Required Attributes
KEY=key-name. The key being identified. Valid values are Attn, Enter, F1–F24, Help, Home, Print, Page Down, Page Up, and Sysreq.
HELP=help-module-name. Links to the help information associated with this key. The associated help text will be defined in a panel group located elsewhere in the menu source or can be imported from another panel group.
ACTION='action-text'. The value specified in the action text defines what happens when the key is pressed. The following are valid values for the action text on a UIM menu:
- ACTIONS switches the cursor position between the panel and the menu bar; it also removes, if shown, a pull-down menu from the panel.
- CALL calls an specified program.
- CMD submits an AS/400 CL command (or System/36 environment OCL command) to the system for processing.
- CMDLINE displays a pop-up window with a command line.
- EXIT returns the user from a group of displays or menus.
- HELP Displays help information for the panel, based on the position of the cursor.
- HOME displays the initial (home) menu of the job.
- MENU displays a subsequent menu as a result of selecting a menu item or pressing a function key.
- MOREKEYS displays an additional set of active function keys and their descriptions; it's used when all keys cannot be shown at once.
The ACTION attribute is the key to using dynamic menu documentation. If you're using green-screen help panels as the basis for your menu documentation, the key item definition for the help action would be set as shown here:
:KEYI KEY=F1
HELP=helpf1
ACTION=HELP
We can also execute other tasks from the ACTION attribute, including calling programs as shown here:
:KEYI KEY=F1
HELP=help
ACTION='CMD CALL PGM(mypgm)'
This example will result in the program mypgm being called when the F1 or HELP key is pressed.
Now it's time to explore how to use this capability to launch the help documentation.
Launching Help Documentation
The concept here is pretty simple. The menu documentation is generated as an HTML file, which is saved to either a shared network drive or a Web server. You need a program to allow you to launch that HTML file. That program is shown below:
PGM PARM(&MENU)
DCL VAR(&MENU) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(10)
DCL VAR(&CMD) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(123)
CHGVAR VAR(&CMD) VALUE('rundll32 +
url,FileProtocolHandler +
"http://webserver/helptext/' *TCAT &MENU +
*TCAT '.html"')
STRPCO
MONMSG MSGID(IWS4010)
STRPCCMD PCCMD(&CMD) PAUSE(*YES)
ENDPGM
Note that this program assumes that your client supports the PC Organizer application. The program expects a single parameter that identifies the menu name for which the help is to be displayed. That value is then used as part of the URL for the HTML document to display. This assumes that you save your HTML documentation using the same name as the menu associated with the documentation. For example, if you had a menu named MAINMENU, the documentation would be saved so that it would be accessible from the following URL: http://webserver/helptext/mainmenu.html.
In this example, the server name webserver would be replaced by the name of your Web server. I've added a folder helptext to the path simply to illustrate that you would probably want to isolate your documentation into its own folder. When this program is called, it utilizes the Windows rundll32 command to launch the supplied URL via the Windows FileProtocolHandler. This is the same functionality that Windows uses to determine what application to launch based on a supplied file type. In this case, the client's Web browser will be launched to display the HTML page.
Putting It All Together
To see how to call the MENUHELPCL program from the menu help key, take a look at the example UIM menu source program shown below:
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:PNLGRP.
.*
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
.* Copyright notification displayed in the message area
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:COPYR.
(C) Copyright Mike Faust 2011
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
.* UIM Z-variable to be used as the panel identifier
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:VAR NAME=ZMENU.
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
.* UIM Z-variable to be used as the panel identifier
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:KEYL NAME=menukeys
HELP=keyl.
:KEYI KEY=F1
HELP=help
ACTION='CMD CALL PGM(MUHELPCL) PARM(SMPLMENU)'
VARUPD=NO.
F1=Help
:KEYI KEY=F3
HELP=exit
ACTION='EXIT SET'
VARUPD=NO.
F3=Exit
:KEYI KEY=ENTER
HELP=enter
ACTION=ENTER.
:EKEYL.
:PANEL NAME=MYMENU
HELP='MENU/help'
KEYL=menukeys
ENTER='MSG CPD9817 QCPFMSG'
PANELID=ZMENU
TOPSEP=SYSNAM.
Sample Menu
.*
.* -------------------------------------
.* Define the menu area
.* -------------------------------------
:MENU DEPTH='*'
SCROLL=NO
BOTSEP=SPACE.
:TOPINST.Select one of the following:
.*
.* -------------------------------------
.* Specify the action to be taken for each option
.* -------------------------------------
:MENUI OPTION=1
ACTION='MENU MAIN'
HELP='MENU/option1'.
Main Menu
:MENUI OPTION=2
ACTION='CMD CALL PGM(MYPGM) PARM(PARM1)'
HELP='MENU/option2'.
Run Program MYPGM
:EMENU.
.*
.* -------------------------------------
.* Use a command line and allow commands and option numbers
.* -------------------------------------
:CMDLINE SIZE=LONG.
Selection or command
.*
:EPANEL.
.*
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
.* Define help modules for the menu panel
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:HELP NAME=keyl.
Function Keys - Help
:XH3.Function keys
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME=exit.
:PARML.
:PT.F3=Exit
:PD.
Ends the current task and returns to the display from which the
task was started.
:EPARML.
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME=customkey.
:PARML.
:PT.F13=Custom Key Action
:PD.
This key performs a custom action.
:EPARML.
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME='MENU/help'.
Sample Menu - Help
:P.
Sample Menu
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME='MENU/option1'.
Go to another menu,
:XH3.Go to menu MAIN.
:P.
This is the help text for option 1.
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME='MENU/option2'.
Run a program
:XH3.Run MYPGM
:P.
This option runs the program MYPGM.
:EHELP.
.*
:HELP NAME='enter'.
Enter Key Help Text
:XH3.Enter Key
:P.
Press the enter key to execute an option or command.
:EHELP.
.*
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
.* End of menu source
.* -----------------------------------------------------------------
:EPNLGRP.
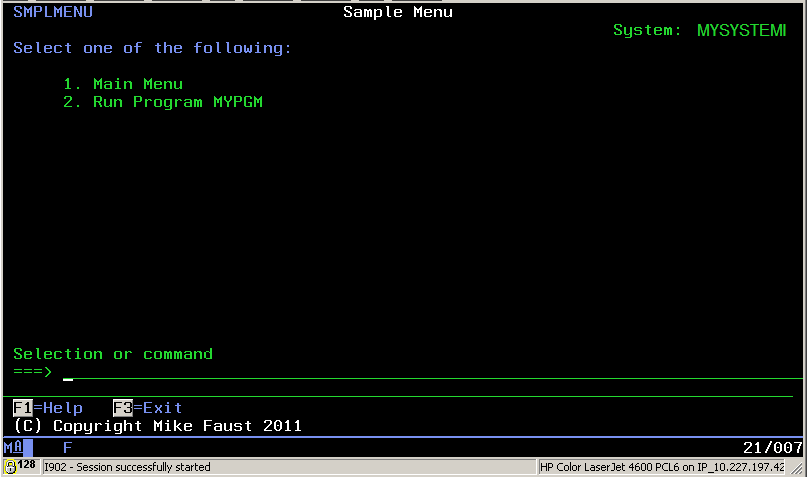
Note that the definition of the ACTION attribute for the KEYI associated with the help (F1) key is defined as 'CMD CALL PGM(MENUHELPCL) PARM(SMPLMENU)'. This defines that the menu should call the HELPMENUCL program passing the menu name (SMPLMENU) as the single parameter. Figure 2 shows the green-screen representation of this menu.
Figure 2: This is a very simple UIM menu. (Click images to enlarge.)
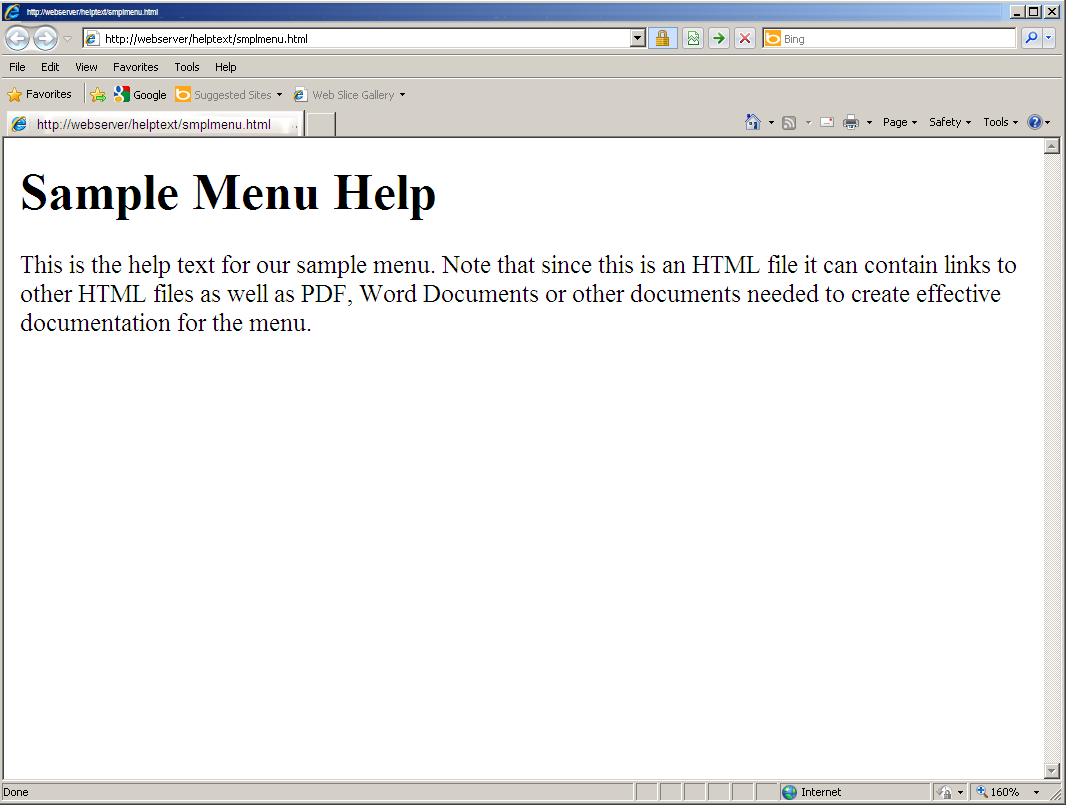
When a user presses the F1 Key for help on this menu, a Web browser is launched and the documentation shown in Figure 3 is displayed.
Figure 3: This is a sample of the document displayed by the help function.
It's also possible to launch other types of documents in the same way simply by changing the path or file type. The code below shows a replaced version of the command launched in the MENUHELPCL program:
CHGVAR VAR(&CMD) VALUE('rundll32 +
url,FileProtocolHandler +
"\\networkserver\share\Documentation\' *TCAT &MENU +
*TCAT '.pdf"')
In this example, the code opens a PDF file stored on a network shared drive identified by the UNC path \\networkserver\share under the Documentation folder. The result is the same in that the required document is launched when the user presses the Help key.
The code for the MENUHELPCL program can be found here.
Documentation or Document-ation
Whether you use an HTML file or a PDF file, or even if you get more advanced and store your system documentation in a database and display the results using an ASP or PHP script, the ability to display custom documentation from a System i menu using the Help key will allow you to implement more dynamic usable system documentation with only a few keystrokes.
















 Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new.
Business users want new applications now. Market and regulatory pressures require faster application updates and delivery into production. Your IBM i developers may be approaching retirement, and you see no sure way to fill their positions with experienced developers. In addition, you may be caught between maintaining your existing applications and the uncertainty of moving to something new. IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
IT managers hoping to find new IBM i talent are discovering that the pool of experienced RPG programmers and operators or administrators with intimate knowledge of the operating system and the applications that run on it is small. This begs the question: How will you manage the platform that supports such a big part of your business? This guide offers strategies and software suggestions to help you plan IT staffing and resources and smooth the transition after your AS/400 talent retires. Read on to learn:
LATEST COMMENTS
MC Press Online